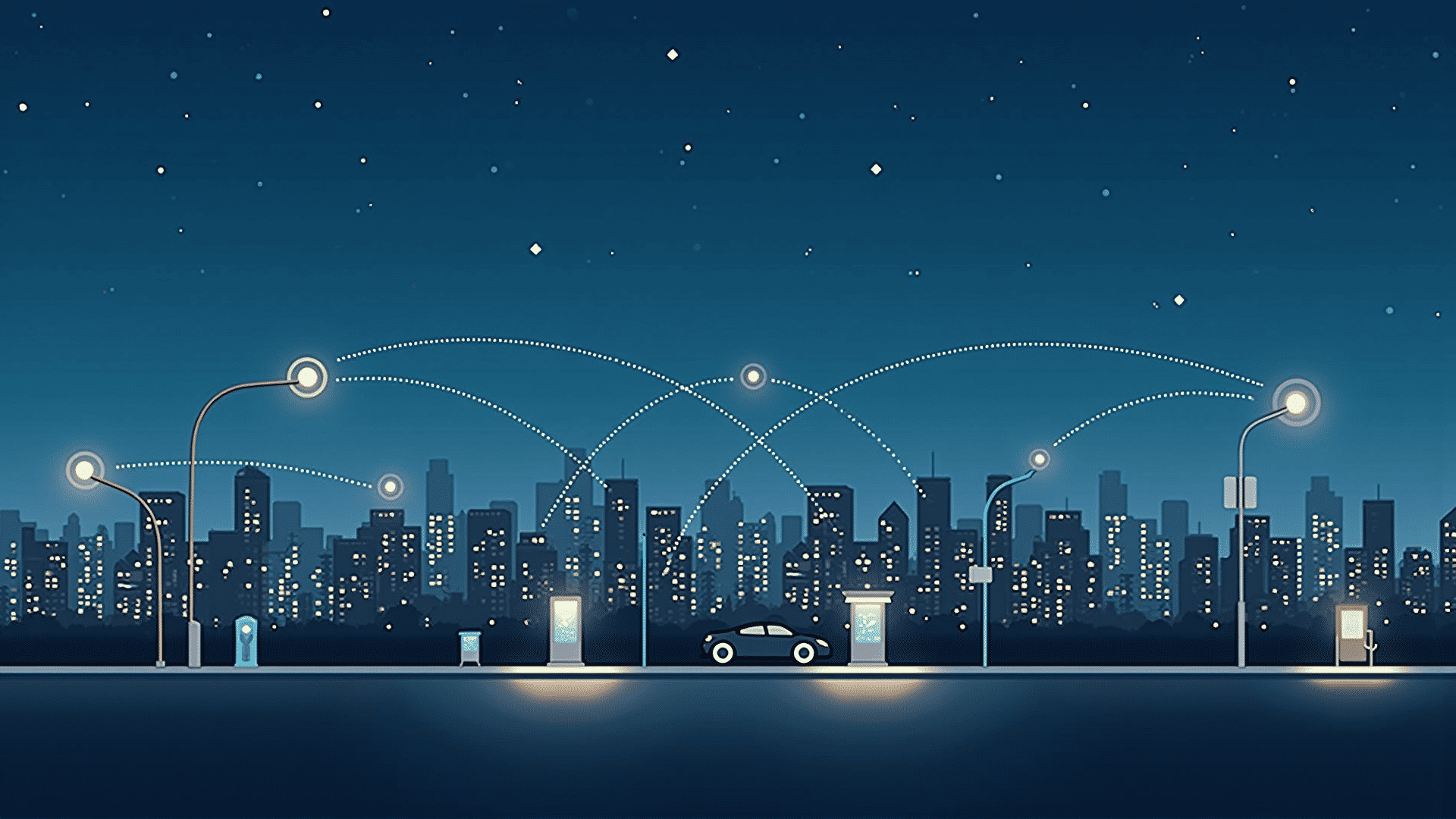
Edge computing is rapidly changing the landscape of data processing and technological infrastructure. Unlike traditional computing models that centralize data processing in large data centers, edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed. This approach significantly reduces latency, enhances real-time data handling, and improves overall efficiency.
The core idea behind edge computing is to minimize the distance data must travel and thus reduce the time it takes for information to circulate between the source and the processing centers. This is particularly crucial in environments where real-time processing is vital, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation. By processing data near the source, edge computing allows for instant decision-making, which is essential in critical applications that rely on rapid response times.
One of the primary sectors reaping the benefits of this technological shift is the Internet of Things (IoT). The vast network of IoT devices generates an enormous amount of data that needs to be processed quickly and efficiently. Edge computing addresses these needs by providing a decentralized architecture where processing occurs at or near the data source. This setup not only conserves bandwidth but also enhances security, as data does not need to travel long distances to data centers.
In addition to IoT, industries such as healthcare are also experiencing transformation through edge computing. Medical facilities often require quick processing of data from various sources, such as patient monitoring systems. Edge computing enables health professionals to access and analyze data in real-time, enhancing patient care by facilitating quicker diagnostics and tailored treatments.
The entertainment industry, too, is leveraging edge computing to provide enhanced user experiences. With the rise of augmented reality and virtual reality, reducing latency is essential to ensure smooth and immersive experiences for users. Edge computing allows for localized data processing, which means users can enjoy high-quality content without delay, irrespective of their location.
Lastly, edge computing supports sustainability by reducing the energy consumption associated with data transmission. By limiting the data that needs to be sent over long distances, it minimizes the energy required for data transport and consequently lessens the environmental impact. This efficiency is critical for supporting sustainable practices across various sectors.
In summary, edge computing is a pivotal advancement in technology, streamlining operations across multiple industries by bringing computational power closer to where it is needed. Its impact extends beyond mere efficiency; it enhances safety, security, and user experience while promoting sustainable practices. As edge computing technology continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future of data processing and connectivity.